With the world we are heading towards, in terms of global warming and environmental concerns, it is high time that we start thinking of more sustainable options in our everyday life. We have reached a stage where there is a dire need for sustainability to better our tomorrow.
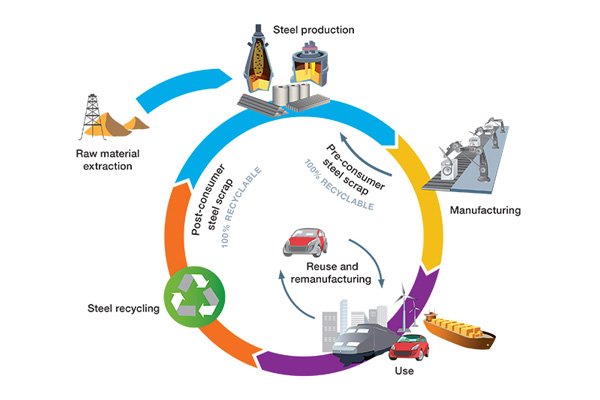
As we make a shift from the products that we use on a daily basis, based on how sustainable they are, steel plays an important role. Steel is one of most heavily recycled materials in the world and it can be recycled almost indefinitely without losing any of its properties. Here is the life cycle of steel to understand how it works as a sustainable metal.
- Responsibly getting raw materials. The first step in the production of steel is getting hold of the raw material in a manner that is sustainable and responsible, therefore causing the least amount of damage to the environment.
- The second step is the efficient production of steel. The next important step within the life cycle of steel is to actually produce the steel from the raw materials, effectively and efficiently. There are two different ways through which this product can be done. Other through iron-ore based production in blast furnaces, or scrap-based production. It is within the space of iron-ore based productions that companies have the opportunity to improve and be more environmentally effective. Technology in the iron-ore based production of steel needs to be constantly improved to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide emissions.
- The next step in the production of steel is obviously the use of the same. Steel is a commonly used metal and is extremely strong. It has multiple uses, a lot of which we are aware of the everyday products that we use. These range from the body of cars to the utensils in our household. It is crucial here that energy-efficient methods are used during the manufacture of steel-based products.
- Once the steel has been used, there is the recirculation of residual steep production. Wherever possible, residuals from steel making are recirculated, in a manner wherein they substitute virgin raw materials. Most of the dust created in the process of making steel is reused for the same process. This leads to a decrease in the amount of waste being produced.
- Finally, the final products which were made, once they run their course, can be recycled multiple times, without loss of original properties.