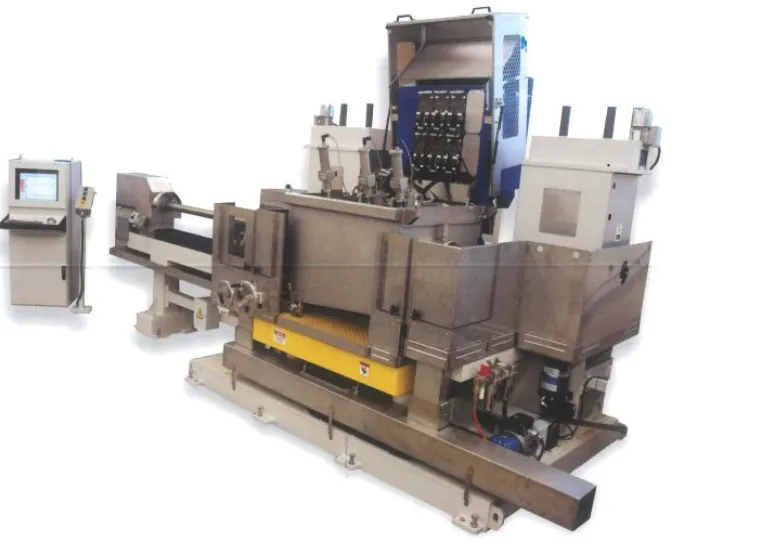
Steel is one of the most pervasive materials used around us. From large plants to a small screw, everything has steel in it. It is one of the most important materials required in industries like construction, manufacturing etc. Sunflag takes a chance to explain the difference between when free and semi-free steel is used.The advantages of steel are its tensile strength and that the cost of production is lower than many other materials. It largely comprises of carbon and iron. Over the years, technology has advanced and many breakthroughs have happened. Even in the steel industry, different kinds and grades of steel are being produced. Free cutting steel is one such kind of steel. Free cutting steel are those iron – carbon alloys that are easy to be worked upon during machining operation. Machinability is the main property required for this kind of steel. In more technical terms free cutting steel has more Sulphur content in it than the carbon content. Free cutting steel has a higher percentage of Sulphur and phosphorus which is different from steel that has a higher percentage of carbon. These steels are defined in standard EN10087. They are divided into steels not intended for heat treatment, for case hardening or for direct-hardening steels. The high Sulphur and phosphorus content in free cutting steel makes it easy to cut through this kind of steel. This property of Free cutting steel makes its application very important in the manufacturing industry. Furthermore, Free cutting steel is mixed with tellurium to make an alloy, and to make it strong and solid. This enhances the mechanical property of the free cutting steel. Some essential criteria for making free cutting steel are
- Tool wear as low as possible during cutting times
- Sufficient surface quality
- Low cutting forces and temperature to allow for the application of sensitive cutting tools and machines.
- Short, light breaking chips to ensure undisturbed chip removal
These properties make for better application of free cutting steel. Considering that free cutting steel has good machinability qualities, its use and application is suitable where good machinability is an important criterion. They are used for rapid production on single, or multiple spindle automatic lathe and capstan lathes of finely finished components which will not be subjected to high stress when in use. Some of these uses include light duty studs, cycle components, and many intricate parts for textile and printing machinery. The use and applications of free cutting steel varies with variation in grading. Bright Bars is a popular type of free cutting steel that has been in the market for some time. These are commonly used by many industries in production of some instruments.
Due to its machinability property, this type of steel forms chips when it is worked on. Hence, they can take up only an average amount of heavy duty items at a time.
The Bright bars are not given any heat treatment and they also involve a very limited amount of tempering so that the stress that forms during its production can be released. In the industry, these free cutting steel Bright bars are used for making nuts, bolts, spare parts for the automobile industries and for making some precision instruments or other kinds of instruments that are being used by several companies.There are different kinds of Bright Bars and they have their specific benefitsEN1A – This type of free cutting steel has two options. Leaded free cutting steel and non-leaded free cutting steel found in circular or hexagonal shaped bars in the market. Due to their make, they are fit for making nuts, bolts, and parts for some precision instruments.
EN1AL – The EN1AL are leaded free cutting steel bars. These are steel bars alloyed with lead for its finish and extensive mechanical properties. They have corrosion resistant properties and hence do not rust that easily. Due to these properties, they are used extensively in automobile parts production.
EN8M – This type of steel comprises of Sulphur with a small amount of carbon, are mostly round or hexagonal in shape, and are used for making shafts, gears, studs, pins gears.