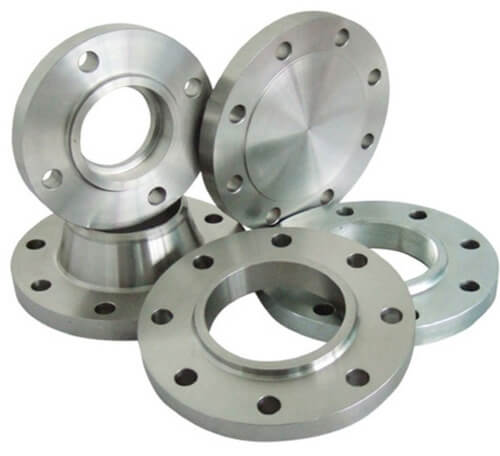
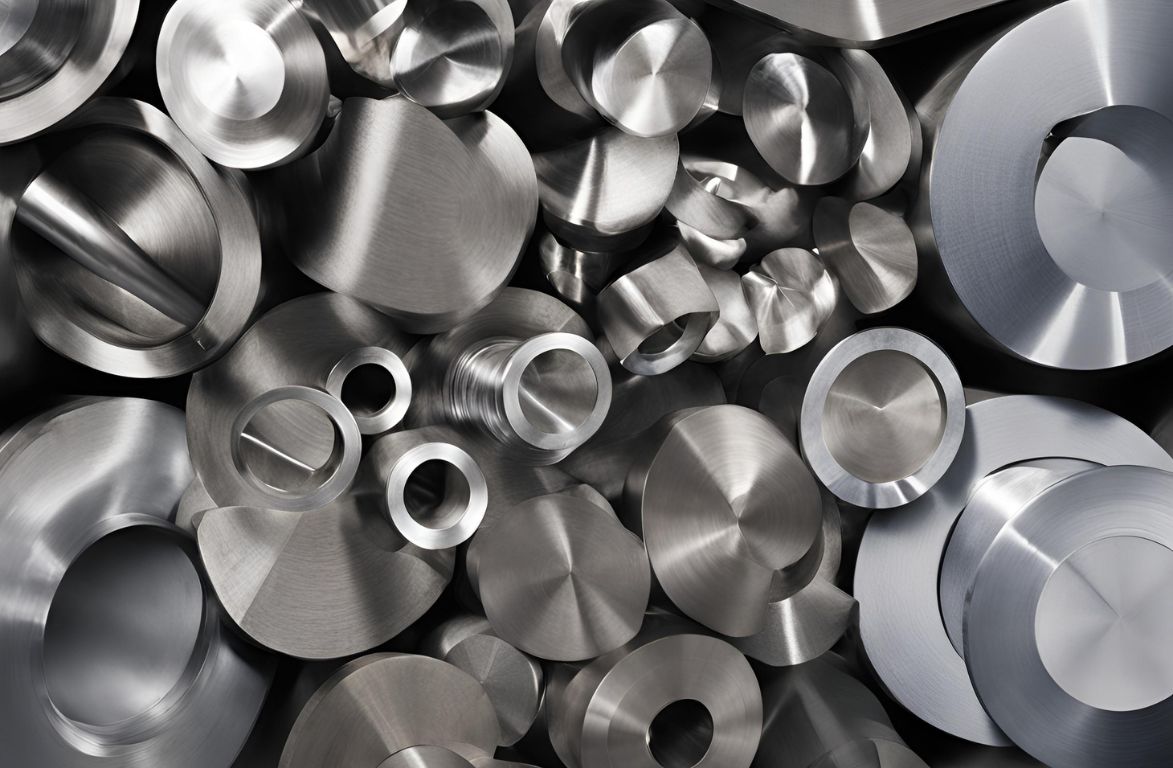
Steel flanges are one of the most useful steel inventions in the world of machinery. Albeit only a connecting material, their design plays a massive role in how the entire machine functions. Flanges are metal rings – either forged or cast – which connect sections of pipes, or join the pipe to a pressure valve or another equipment piece. They are also used in sports equipment (such as skis) or in train wheels and tracks, for the smooth motion they provide
Flanges are considered an internal component, and make it very easy for machine maintenance to take place. Their structural integrity is dependent on the material they are made of, which in turn, is decided by how the machine itself will be used. They are most commonly made of carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, or steel heavy with titanium and nickel alloys.
One of the main advantages of flanges is that they allow for quick assembly and removal of different parts of a machine. This is crucial, not just for maintenance work, but also for versatility in the machine’s primary functions.
There are different kinds of steel flange, and the type defines the function. For instance:
- Threaded flanges follow a screw-on mechanism, where the flange has threading inside and needs to be fixed to the pipe of the matching size. It helps to avoid welding in most cases.
- Socket Weld flanges are great for small pipe diameters, and where the work is low-temperature, low pressure. They’re fairly simple to install, too.
- Slip-on flanges are one of the most common ones. They’re found in a wide range of sizes and fittings, which makes them easy to use in multiple machinery. Although the installation requires some welding, finding the right size and fitting it on is a fairly easy task.
- Lap joint flanges are a two-piece design. They need butt welding to be connected, but they are excellent for us in restrictive physical spaces. Given that they are in more than one piece, they are also very easy to dismantle.
- Weld neck flanges also require butt welding when being installed. They have high integrity and are preferred in systems that involve high pressure or high temperature work.
- Blind flanges are used to isolate pipe sections. They are blank disks, bolted into place to stop the flow, and act as a seal when installed correctly.