Steel happens to be one of the most versatile alloys in production. Often made from recycled scrap metal, and combined with different metals to create different properties, it is used from structural strength to accessories.
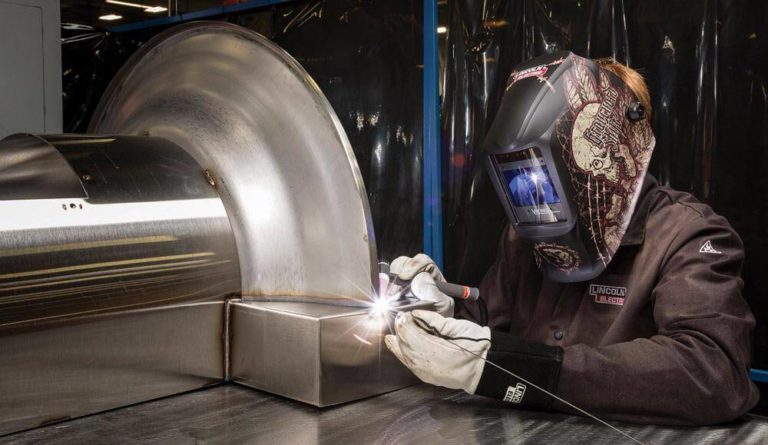
But as helpful as steel is, it would be nothing without the ability to weld it into different shapes and forms. Welding is an integral part of any metallic or alloy creative process, and steel has its own set of rules for which processes to follow. What kind of welding is done depends on the material properties of the steel, its thickness, as well as the finish of the metal?
Deciding which procedure to use starts with knowing which type of joint you are aiming for. Different joints serve different purposes – and the end result will be determined by the material used, as well. You have to consider factors such as strength of material, heat resistance, and how accessible the joint will be upon completion.
The main types of joints are butt, corner, edge, lap, and tee. They can be used in multiple permutations and combinations for a certain desired effect. Once you know which type of joint/joints you are aiming for, you can then decide which process is best suited for your choice of materials.
Don’t fret! We have a helpful guide for you. Sunflag Steel has combined a list for you to understand what some of these procedures of steel welding are.
GAS TUNGSTEN ARC WELDING
Commonly also known as TIG Welding, this is one of the most used forms of welding for stainless steel. It offers a lot of longevity, as well as a high quality end product. Since the heat input level is fairly low, it is ideal for thinner sheets. The method uses argon, and other gases depending on what the intended final product is. These include nitrogen, helium, and hydrogen.
SPOT WELDING
Resistance welding, also known as Spot Welding, is considered to be an extremely cost-effective form of steel welding. It can be used for projects of different scales, making it flexible in its usage range. Resistance welding uses an electric current. The current produces heat, which is used to melt and seal the edges of frayed metal. It is useful for steels that have a lower melting point because it can also prevent warping of the raw material.
MIG WELDING
Gas Metal Arc Welding is also called MIG welding (Metal Inert Gas), because of the gas used in this process. It is a relatively semi-automatic process. Since the method uses an electric supply, it’s much preferred for very specific welding in spots where other methods can’t easily reach. Sometimes other gases are added to the mix to further stabilize the current.
PLASMA ARC WELDING
This process is actually derived from TIG welding. It involves a nozzle that produces a plasma arc. This arc penetrates the steel and allows it to fuse together. This method is frequently used in more mechanical welding processes, where there is need for high speed movement and high productivity.
SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
Shielded Metal Arc Welding might be one of the oldest welding processes for steel. It involves electrodes, and is a fairly manual process. The coating of the electrodes is decided based on what the use for the welding is – what is the composition of the steel being welded, and what are the desired characteristics in the electrode upon use.
FLUX CORED WELDING
Flux Cored Welding was developed as an alternative to Shielded Metal Arc Welding. It is derived from the MIG process, but instead of a solid wire, there is a flux or a metal powder used in the tube. There are two wires produced, and are used according to the demand of the procedure. The flux provides a higher degree of stabilization, shielding, and de-oxidization. There is also a massive reduction of fumes produced in this procedure. It is mostly used in construction projects.
ELECTRIC RESISTANCE WELDING
This form of steel welding is only used for mass production and welding of thinner material. It exists to prevent the crevice from detracting from corrosion resistance.
With Sunflag Steel we get you the best quality steel services for our customers with enhances capabilities.